Androgenic Alopecia: What It Is and Why It Matters
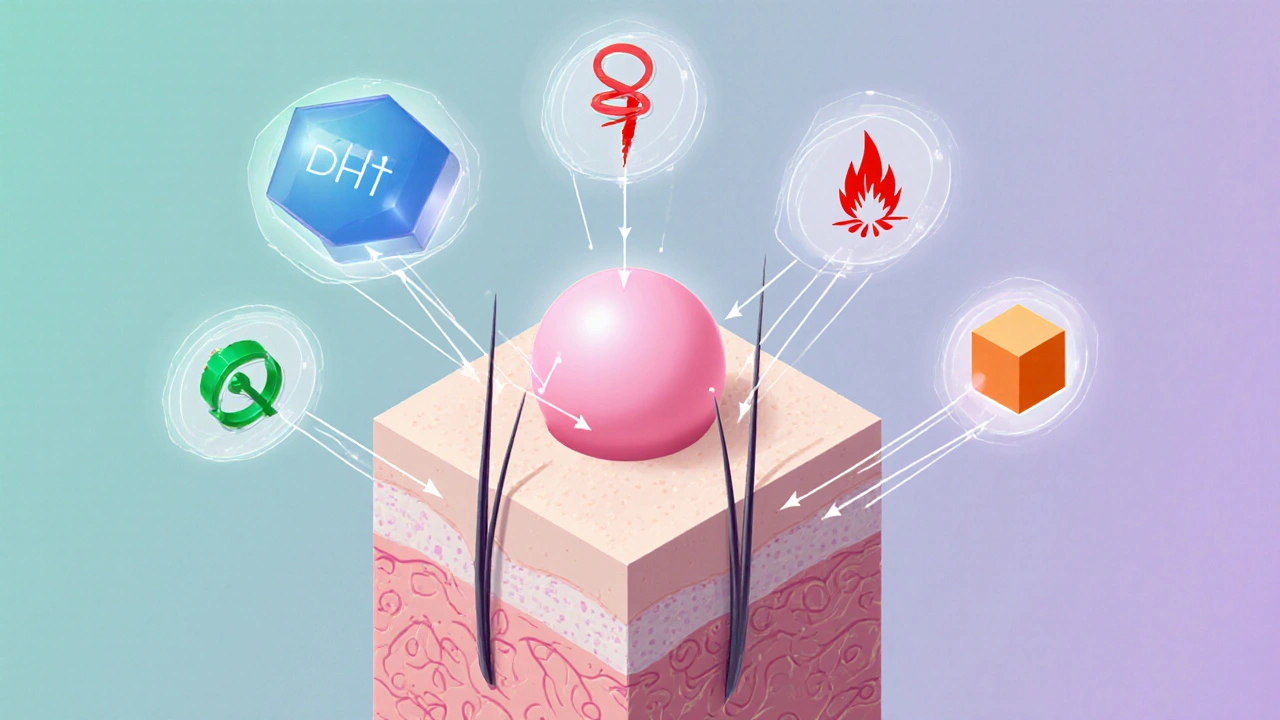
When dealing with Androgenic Alopecia, a progressive thinning of the scalp hair driven primarily by hormonal factors. Also known as male pattern baldness, it affects both men and women, though patterns differ. The core trigger is Dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a derivative of testosterone that binds to hair‑follicle receptors and shortens the growth phase. In simple terms, higher DHT levels push follicles into a “shrinking” state, leading to the classic recession at the temples and crown.
Key Players in Managing Androgenic Alopecia
Understanding the condition opens the door to several proven approaches. Finasteride works by blocking the enzyme 5‑α‑reductase, which converts testosterone into DHT. By lowering scalp DHT, finasteride can halt further loss and even regrow some hair. Minoxidil takes a different route: it widens blood vessels around follicles, improving nutrient delivery and stimulating the anagen (growth) phase. Many users combine both for a synergistic effect—finasteride tackles the cause, while minoxidil boosts the response.
For those seeking a more permanent visual fix, Hair Transplant moves healthy follicles from a dense donor area to balding zones. Modern grafting techniques like FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction) preserve natural hair angles, making results look seamless. Alongside medical options, nutritional support matters: supplements rich in biotin, zinc, and saw‑palmetto are often recommended to reinforce follicle health, though they work best when DHT levels are already managed.
All these strategies share a common goal—restore confidence by slowing or reversing the thinning process. Below you’ll find articles that break down dosing tips, safety notes, and real‑world buying guides for the drugs and supplements mentioned. Whether you’re just noticing a widening part or you’ve hit the vertex, the collection offers practical steps to tackle androgenic alopecia head‑on.