Hair Loss Hormones: What Drives Thinning and How to Manage It
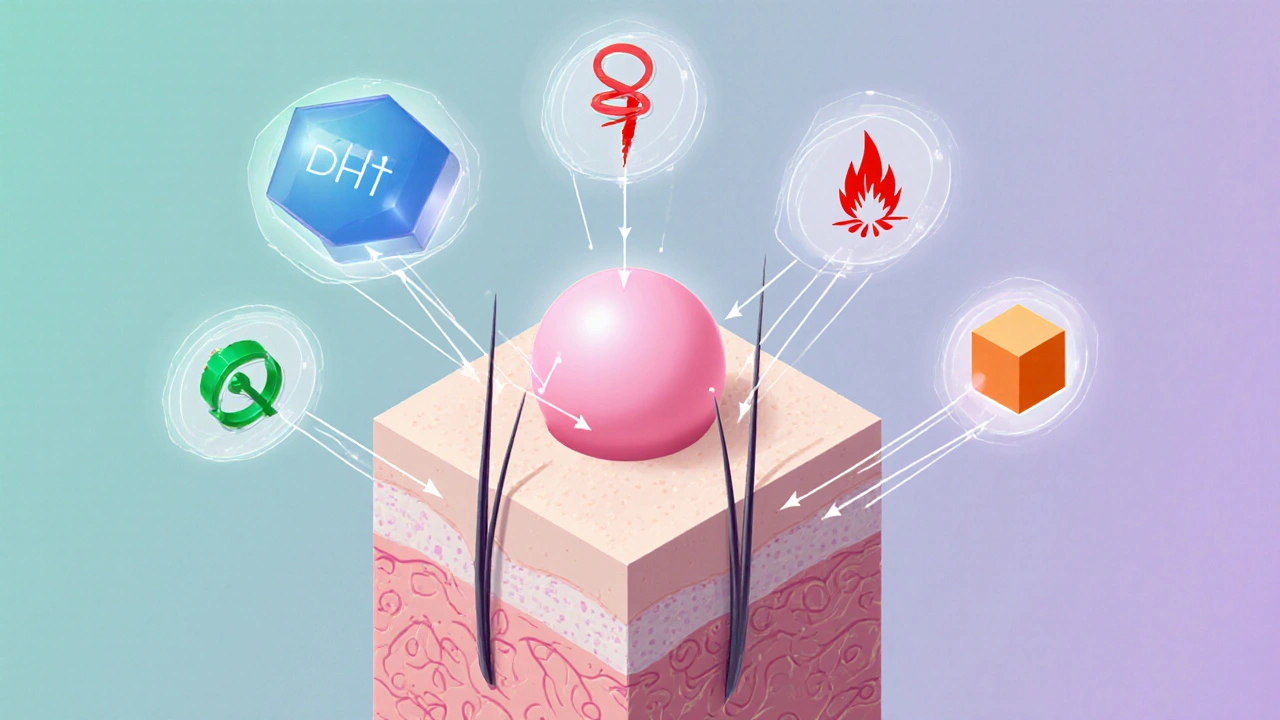
When you hear the term hair loss hormones, the chemicals that speed up or slow down the hair‑growth cycle, you might picture a mysterious culprit behind every bald spot. In reality, these hormones are ordinary messengers your body uses every day. They tell follicles when to grow, rest, or shed. Knowing which hormones are at play helps you spot the real reasons behind your thinning hair and choose the right steps to fight it.
Key Hormones and Their Impact
One of the biggest players is testosterone, a male‑dominant hormone that also exists in women in smaller amounts. Your body can convert testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a more potent form that binds tightly to hair‑follicle receptors. The conversion creates a clear semantic triple: testosterone → converts to → DHT. DHT then shortens the active growth phase of follicles, which is why many men notice a receding hairline in their twenties. If you’ve ever taken a DHT‑blocking shampoo, you’ve been targeting this exact pathway.
On the flip side, estrogen, the primary female sex hormone that also appears in men can act like a buffer. Estrogen competes with DHT for the same receptors, often slowing down the miniaturization of hair follicles. That’s why some women experience less aggressive thinning during pregnancy when estrogen levels soar. The relationship forms another triple: estrogen ↔ moderates ↔ DHT activity. Understanding this balance lets you consider lifestyle tweaks, like diet or supplements, that naturally support estrogen’s protective role.
Beyond sex hormones, thyroid hormones, thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) that regulate metabolism are crucial for a healthy scalp. An underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism) can stall the growth phase, while an overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism) may cause rapid shedding. The third semantic link looks like: thyroid hormones → regulate → hair‑growth cycle. Simple blood tests can reveal if a thyroid issue is behind unexpected hair loss, and correcting the hormone levels often restores normal growth.
All these hormones don’t work in isolation. A shift in one can ripple through the others, creating a cascade that either accelerates or slows hair loss. For instance, stress can raise cortisol, which in turn nudges testosterone toward more DHT production. Knowing these connections equips you to address the root cause rather than just the symptom.
Below you’ll find a curated list of articles that dive deeper into each hormone, explain how medications and natural remedies interact with them, and offer step‑by‑step plans to keep your follicles thriving. Whether you’re looking for medical‑grade options, over‑the‑counter solutions, or lifestyle adjustments, the posts ahead cover the full spectrum of strategies for tackling hair loss at its hormonal source.