Understanding Reperfusion Injury and Its Effects
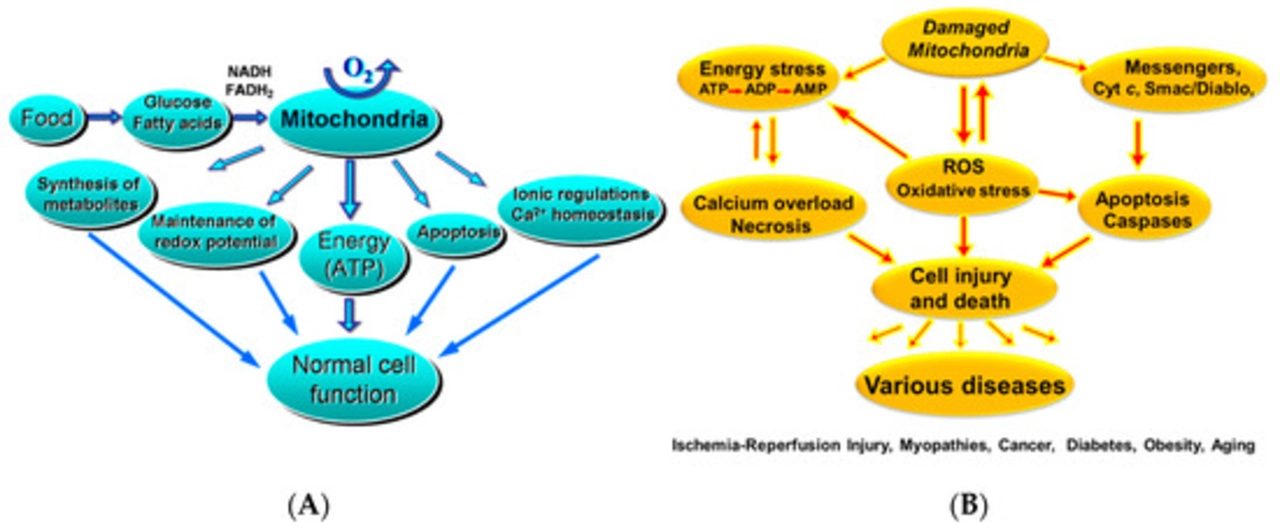
Before diving into the role of antioxidants in preventing reperfusion injury, it's essential to understand what reperfusion injury is and how it affects our body. Reperfusion injury occurs when blood supply returns to the tissue after a period of ischemia, or lack of oxygen. The sudden influx of oxygen and nutrients can cause a series of damaging reactions, leading to cell death and tissue damage. This phenomenon is commonly observed in heart attacks, strokes, and organ transplants.
In this article, we will explore the role of antioxidants in preventing reperfusion injury and their potential benefits in maintaining our overall health. So, let's get started!
Free Radicals: The Culprits Behind Reperfusion Injury
One of the primary factors contributing to reperfusion injury is the production of harmful molecules called free radicals. These unstable molecules are formed during the process of reperfusion and can cause significant damage to cells and tissues. Free radicals have unpaired electrons, making them highly reactive and prone to causing oxidative stress, which can lead to cell death and tissue damage.
Fortunately, our body has a defense system to neutralize free radicals and protect our cells from oxidative damage. This is where antioxidants come into play.
Antioxidants: Our Body's Natural Defense Against Oxidative Stress
Antioxidants are molecules that can neutralize free radicals by donating an electron, thus stabilizing the free radical and preventing it from causing further damage. Our body naturally produces some antioxidants, while others can be obtained through our diet. Some well-known dietary antioxidants include vitamins C and E, beta-carotene, and selenium.
By neutralizing free radicals, antioxidants play a crucial role in preventing the harmful effects of reperfusion injury and maintaining overall health.
The Protective Effects of Antioxidants on Heart Health
Reperfusion injury is a significant concern in the case of heart attacks, where blood flow to the heart muscle is suddenly restored after a blockage. Antioxidants have been studied extensively for their potential to reduce the damage caused by reperfusion injury in the heart. Research suggests that antioxidant therapy can help minimize the extent of heart tissue damage, improve heart function, and reduce complications associated with heart attacks.
Some common antioxidants with potential cardioprotective effects include vitamin C, vitamin E, and coenzyme Q10.
Antioxidants and Stroke Recovery
Similar to heart attacks, reperfusion injury can also occur during a stroke when blood flow is restored to the brain after a temporary blockage. Antioxidants may help reduce the damage caused by reperfusion injury in stroke patients, potentially leading to better recovery and reduced long-term complications.
Studies have shown that antioxidant therapy, particularly with compounds like edaravone and N-acetylcysteine, can improve stroke outcomes by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation in the brain.
Organ Transplants and the Role of Antioxidants
Reperfusion injury is a critical concern in organ transplantation as well. When a donated organ is reconnected to the blood supply, reperfusion injury can cause significant damage to the organ, potentially leading to transplant failure. Antioxidants have been investigated for their potential to reduce reperfusion injury and improve organ transplant outcomes.
Research suggests that antioxidant therapy, including the use of compounds like allopurinol and superoxide dismutase, can help protect transplanted organs from reperfusion injury and improve their function after transplantation.
Dietary Sources of Antioxidants: What to Eat for Optimal Protection
As mentioned earlier, many antioxidants can be obtained through our diet. To ensure that you're getting enough antioxidants to protect your body from reperfusion injury, it's essential to consume a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats. Some antioxidant-rich foods include berries, citrus fruits, leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and fish.
By consuming a balanced and varied diet, you can ensure that your body has the necessary antioxidants to combat oxidative stress and reduce the risk of reperfusion injury.
Conclusion: The Future of Antioxidant Therapy in Preventing Reperfusion Injury
Antioxidants play a vital role in protecting our body from the harmful effects of reperfusion injury. As research continues to explore the potential benefits of antioxidant therapy in various medical scenarios, it's increasingly clear that these powerful molecules can help reduce tissue damage, improve recovery, and promote overall health.
By understanding the role of antioxidants in preventing reperfusion injury and incorporating them into our daily diet, we can take a proactive approach in maintaining our health and reducing the risk of reperfusion-related complications.