Hormone Imbalance Hair Loss
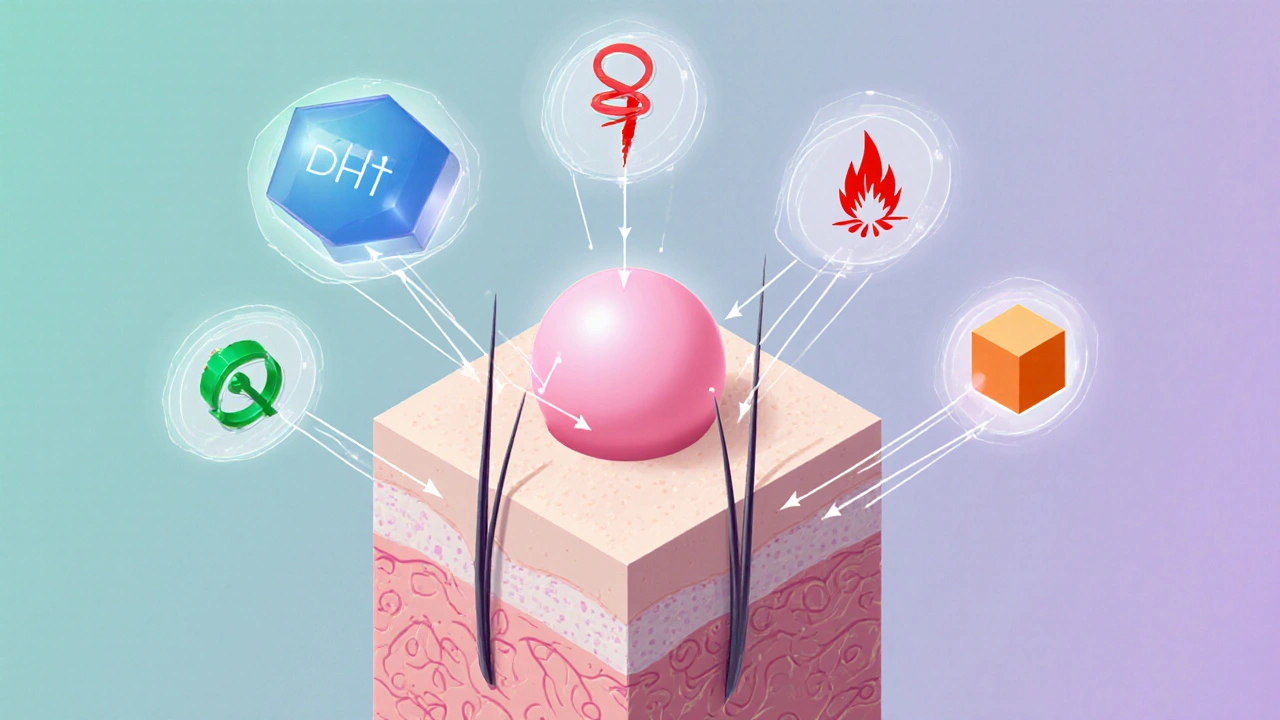
When dealing with Hormone Imbalance Hair Loss, the condition where abnormal hormone levels trigger thinning or shedding of hair on the scalp. Also known as hormonal hair loss, it can affect men and women of any age. The problem usually stems from disrupted Hormones, chemical messengers that regulate growth, metabolism and stress responses, especially Thyroid Hormone, which controls metabolism and hair follicle cycling and Androgens, male‑type hormones like testosterone that convert to DHT and can shrink hair follicles. Understanding how these compounds interact helps you spot the root cause before you start treatment.
Why Hormones Mess Up Your Hair
When the endocrine system goes off‑balance, the hair growth cycle gets interrupted. Hormone imbalance hair loss isn’t a single disease; it’s a symptom that shows up in several scenarios. For example, hypothyroidism slows down metabolism, resulting in brittle, dry strands that fall out easily. Hyperthyroidism, on the other hand, speeds up the cycle, causing rapid shedding. Androgen excess, common in conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or male‑pattern baldness, raises the level of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) that attacks the follicle’s miniaturization process. Stress spikes cortisol, a glucocorticoid hormone that can push hair follicles into a resting phase, leading to diffuse thinning across the scalp. Nutrient deficiencies, insulin resistance and even certain medications (such as some antidepressants, blood pressure drugs, and oral contraceptives) can tilt the hormonal scales further. Menopause adds a drop in estrogen, which usually protects hair, so the relative rise in androgens becomes more apparent. Birth‑control pills that contain synthetic hormones may also shift the balance, sometimes improving and other times worsening hair loss depending on the formulation. The key is to map the specific hormonal culprit—whether it’s thyroid, androgen, cortisol or estrogen—so you can choose a targeted therapy rather than a one‑size‑fits‑all approach. Practical steps start with a blood panel: TSH, free T4, free T3 for thyroid; total and free testosterone, DHEA‑S, and possibly sex hormone‑binding globulin (SHBG) for androgen status; cortisol measured via saliva or serum for stress. Once you have the numbers, your doctor can recommend medication adjustments, hormone‑rebalancing supplements (like biotin, zinc, vitamin D), or lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, stress‑management techniques, and a balanced diet low in refined sugars. Topical treatments like minoxidil work best when the underlying hormonal issue is also addressed, because they only stimulate follicles that are still viable. If you suspect an endocrine disorder, consider consulting an endocrinologist or a dermatologist who specializes in hair loss. They can run a comprehensive work‑up and might suggest therapies such as levothyroxine for hypothyroidism, anti‑androgen drugs like spironolactone for women, or low‑dose oral contraceptives that stabilize androgen levels. In severe cases, platelet‑rich plasma (PRP) injections or hair‑transplant surgery may be options, but they’re most successful when hormones are under control. Lifestyle tweaks can make a noticeable difference. Prioritize sleep to keep cortisol in check, practice mindfulness or yoga to reduce stress, and eat plenty of lean protein, omega‑3 fatty acids, and antioxidants. Avoid harsh hairstyles that pull on the scalp and limit heat styling, which can exacerbate brittle hair already weakened by hormonal imbalances. Gentle, sulfate‑free shampoos and conditioners that contain ingredients like saw palmetto or pumpkin seed oil may offer modest DHT‑blocking benefits. Remember, hair loss often tells a broader story about your overall health. Treating the hormonal imbalance doesn’t just restore a fuller head of hair—it can improve energy levels, mood, and metabolic health. Keep track of changes over weeks rather than days, because hormone‑related hair cycles take time to normalize. Patience combined with a clear diagnosis is your best strategy. Below you’ll find a curated set of articles that dig deeper into specific hormones, disorders, and treatment options. Whether you’re looking for lab‑test guidance, medication reviews, or natural supplement ideas, the collection is organized to help you move from confusion to confident action.