Medication-Induced Delirium: Causes, Risks, and What to Do
When a drug suddenly makes someone confused, disoriented, or hallucinating, it’s often not dementia or a stroke—it’s medication-induced delirium, a sudden change in mental state caused by drugs interfering with brain chemistry. Also known as drug-induced delirium, it’s one of the most preventable causes of acute confusion in older adults and hospital patients. This isn’t just "feeling off"—it’s a medical emergency that can lead to falls, longer hospital stays, or even death if missed.
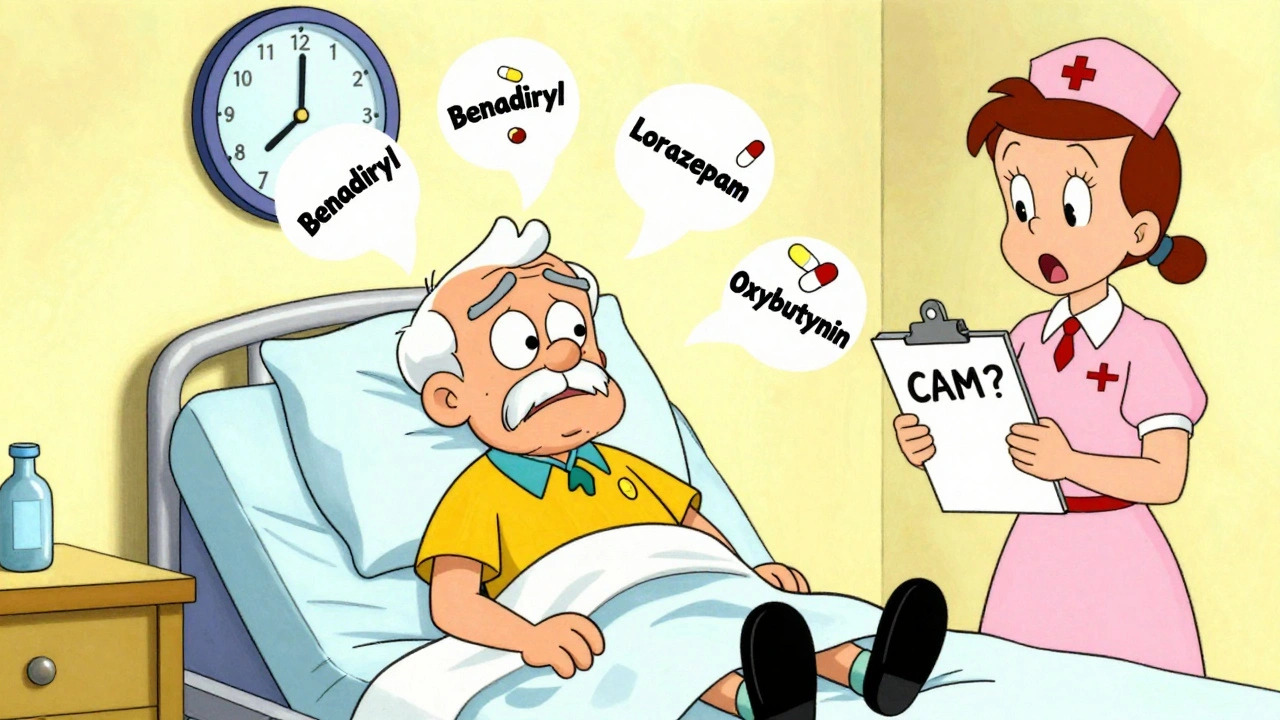
It happens because some medications mess with key brain signals, especially acetylcholine. anticholinergic drugs, a class of medications that block acetylcholine to reduce spasms, saliva, or urine flow are the biggest culprits. Think old-school antihistamines like diphenhydramine (Benadryl), bladder meds like oxybutynin, or even some antidepressants and painkillers. But it’s not just one drug—it’s combinations. Someone on five meds might handle each fine alone, but together they overload the brain’s ability to cope. psychiatric medication risks, especially with sedatives, antipsychotics, or benzodiazepines, are also high on the list. Elderly patients, those with existing brain conditions, or people with kidney or liver problems are at highest risk.
Signs show up fast—within hours or days of a new drug or dose change. The person might forget where they are, mix up day and night, talk nonsense, or see things that aren’t there. They might get agitated or unusually sleepy. Often, families notice it first because the person seems "not themselves." Doctors sometimes miss it, thinking it’s just aging or infection. But if you’ve recently started or changed a medication and someone’s acting confused, don’t wait. Medication-induced delirium can reverse quickly if caught early—often just by stopping or switching the drug.
What you’ll find below are real, practical posts that dig into how drugs trigger confusion, which ones are most dangerous, how to spot the signs before it escalates, and what steps you can take to protect yourself or a loved one. From how dechallenge tests prove a drug caused the problem, to why certain pain meds are riskier than others, these articles give you the facts—not just warnings. No fluff. Just what you need to recognize, question, and act on when a medication doesn’t just treat a problem—it might be creating a worse one.