Amebiasis Prevention
When working with Amebiasis Prevention, the set of actions designed to stop the spread of the parasite Entamoeba histolytica. Also known as amoebic infection control, it involves hygiene, water safety, and proper medication use.
Key Strategies for Prevention
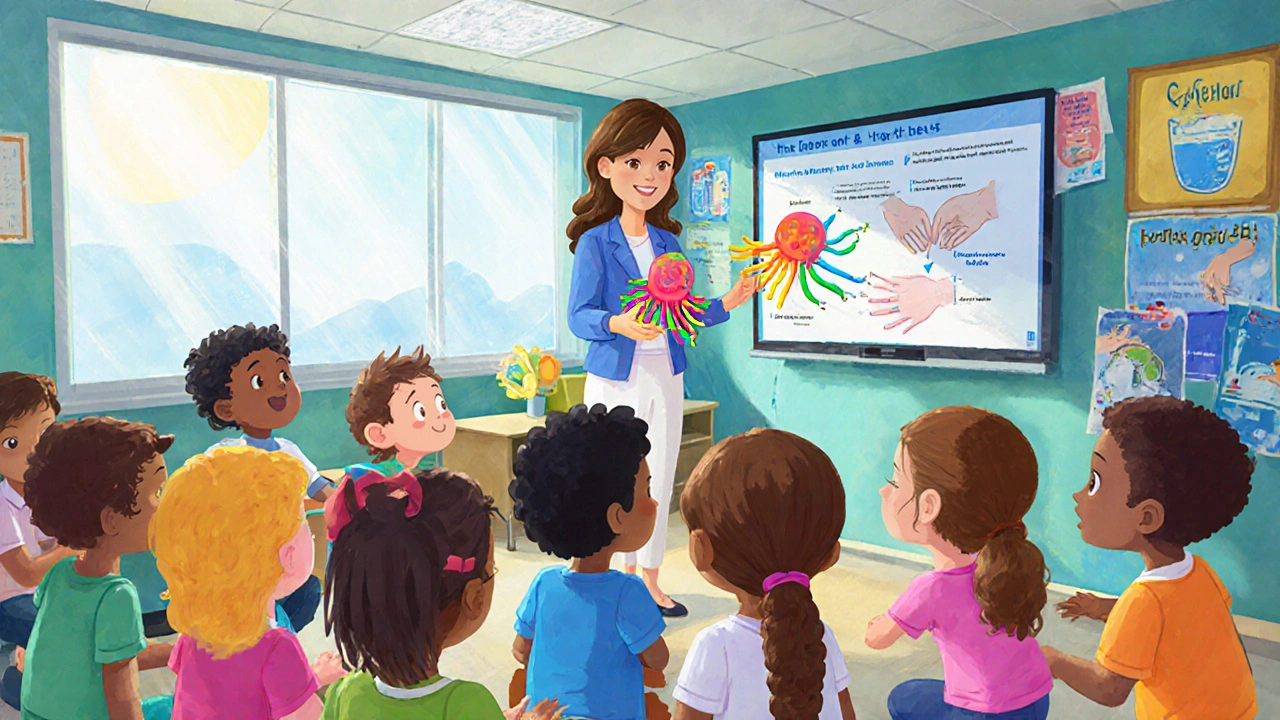
One of the most effective ways to block infection is Water Sanitation, cleaning, treating, and safely storing drinking water. Boiling water for at least one minute or using certified filters removes cysts that cause disease. Pair this with Hand Hygiene, regular washing with soap and clean water after bathroom use or before meals, and you cut the main transmission route. Travelers should treat food and water as potential hazards; that’s where Travel Health, pre‑trip medical advice and preventive measures for travelers comes in. Packing a portable water purifier, avoiding raw salads in high‑risk areas, and asking for bottled water are simple habits that keep you safe.
Even with perfect hygiene, exposure can still happen, so knowing the right medication is crucial. Metronidazole, the first‑line anti‑amebic drug that kills the parasite is prescribed for both treatment and post‑exposure prophylaxis. A typical course lasts 5‑10 days, and adherence prevents relapse. In cases of resistance or intolerance, alternatives like tinidazole are available, but they require a doctor's prescription. The link between proper drug use and reduced disease burden is clear: effective treatment amebiasis prevention relies on timely diagnosis, correct dosing, and patient compliance.
Public health programs tie all these pieces together. Education campaigns teach communities about safe water sources, proper sanitation, and when to seek medical help. Schools that integrate hand‑washing lessons see lower infection rates, illustrating how community‑wide hygiene initiatives influence individual outcomes. Screening high‑risk groups—such as travelers returning from endemic regions or residents in areas with poor sewage systems—helps catch asymptomatic carriers before they spread the parasite. By combining personal habits, medication, and organized health efforts, the spread of amebiasis can be dramatically reduced.
Below you’ll find a curated set of articles that dive deeper into each of these topics, from detailed drug guides to practical travel advice. Use them as a toolbox to build your own prevention plan and stay ahead of the parasite wherever you go.