Benzodiazepines: What They Are, How They Work, and What You Need to Know
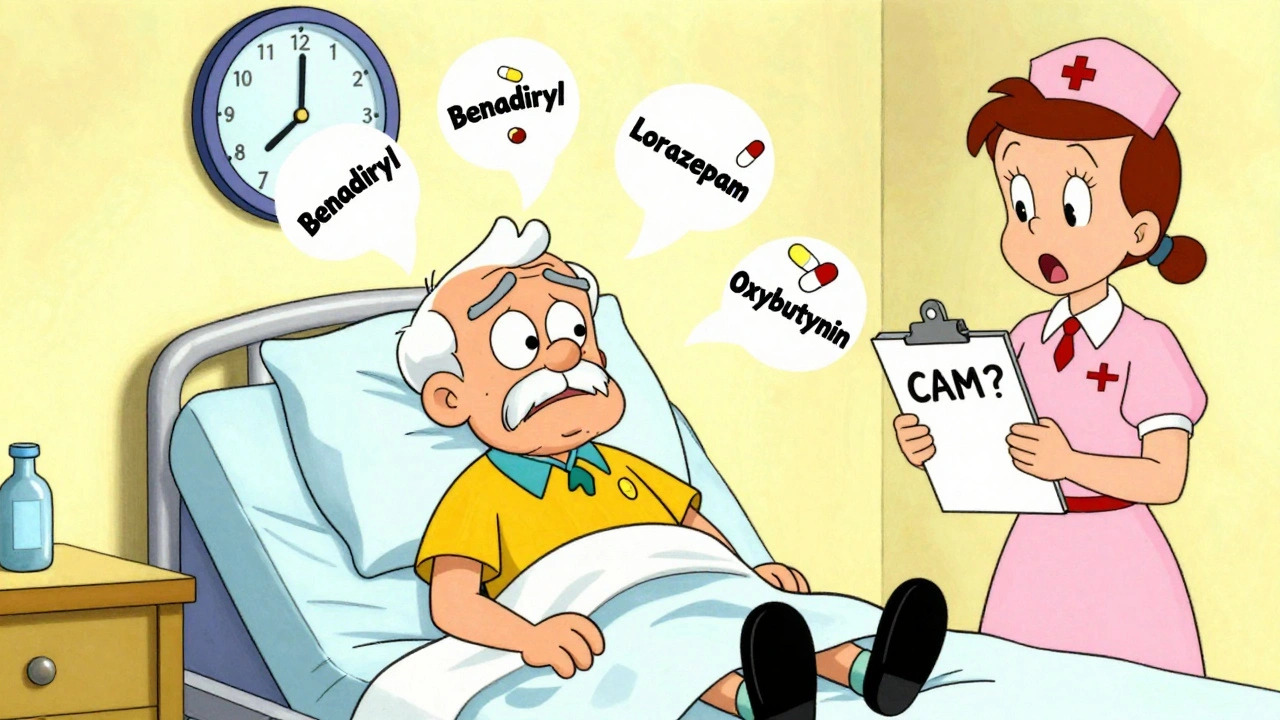
When you hear benzodiazepines, a class of central nervous system depressants used to treat anxiety, seizures, and insomnia. Also known as benzos, they work by boosting the effect of GABA, a calming neurotransmitter in your brain. This is why they help with panic attacks, muscle spasms, and trouble sleeping—but they also carry risks that many people don’t fully understand.
These drugs aren’t all the same. alprazolam, a fast-acting benzodiazepine often prescribed for panic disorder wears off quickly, which can lead to rebound anxiety. diazepam, a longer-acting option used for alcohol withdrawal and muscle relaxation stays in your system for days. Then there’s lorazepam, commonly used in hospitals for acute anxiety or seizures. Each has a different half-life, potency, and risk profile. Mixing them with alcohol, opioids, or even some antidepressants can slow your breathing to dangerous levels—that’s why psychiatric drug interactions are a major concern, as highlighted in multiple studies on medication safety.
Many people take benzodiazepines for a few weeks without issue. But if you’re on them for months or years, your brain starts to adapt. Suddenly, you can’t sleep without them. Or you feel shaky if you miss a dose. That’s not just dependence—it’s physical changes in your nerve cells. Withdrawal isn’t just uncomfortable; it can include seizures, hallucinations, and severe anxiety. Tapering slowly under medical supervision is the only safe way out. And while some turn to natural alternatives like magnesium or cognitive behavioral therapy, those don’t work the same way. Benzodiazepines are powerful tools, but they’re not meant for long-term use.
What you’ll find below are real, practical articles that dig into the details most doctors don’t have time to explain. From how to recognize a class-wide safety alert involving these drugs, to why some people react worse than others due to metabolism differences, to how to track your own use and spot early signs of tolerance—you’ll see how this topic connects to everyday health decisions. These aren’t theoretical guides. They’re based on patient experiences, FDA data, and clinical studies that matter.