Anticholinergic Drugs: What They Are, How They Work, and What You Need to Know
When your body’s anticholinergic drugs, medications that block the neurotransmitter acetylcholine to reduce muscle spasms, secretions, and nerve signals. Also known as cholinolytics, they’re used for everything from treating motion sickness to managing overactive bladder. But here’s the catch: every time you take one, you’re not just calming the target system—you’re also turning down the volume on your brain, gut, and heart. That’s why older adults on multiple anticholinergics are more likely to fall, get confused, or develop memory problems over time.
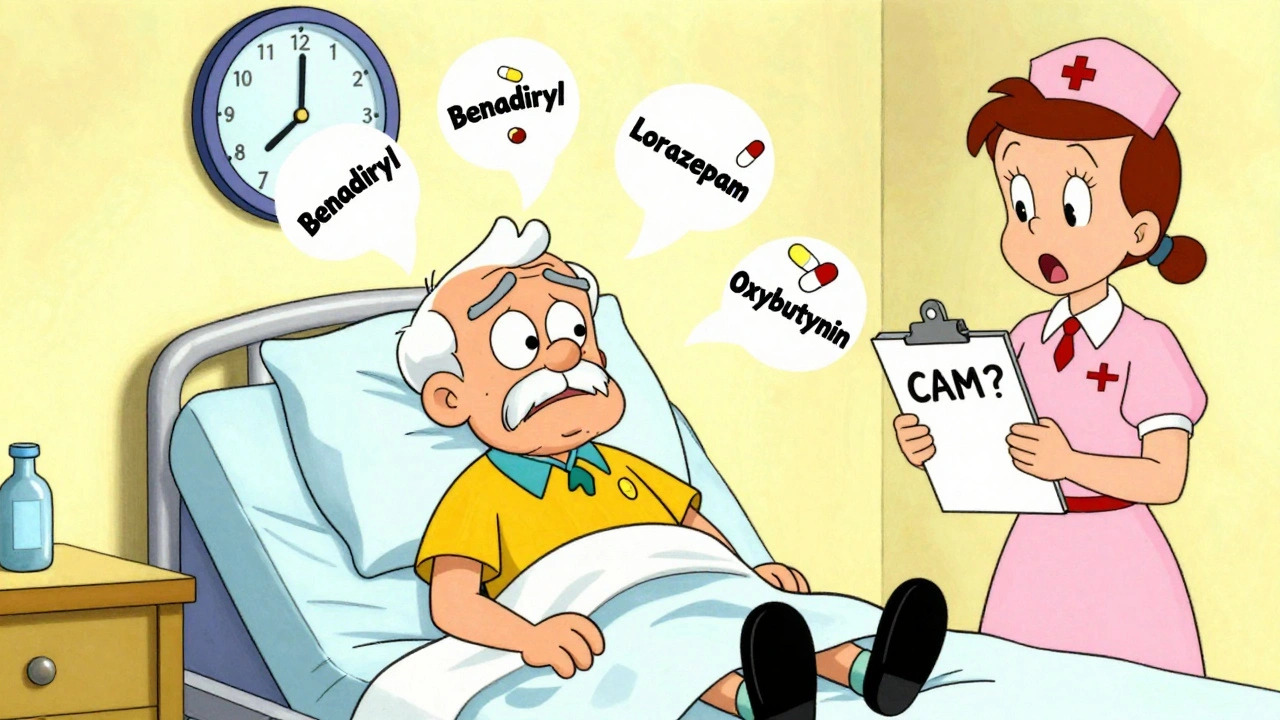
These drugs work by blocking acetylcholine, a key chemical messenger that tells muscles to contract, glands to secrete, and nerves to fire. That’s useful when you have an overactive bladder, Parkinson’s tremors, or severe allergies. But it’s dangerous when you’re also taking other meds that affect the same system. For example, combining an anticholinergic with an antihistamine or a tricyclic antidepressant can pile up the effects, leading to blurred vision, constipation, or even delirium. This buildup is called anticholinergic burden, the total effect of all anticholinergic medications a person takes at once, often measured in clinical studies to predict cognitive decline. A 2019 study in JAMA found that people taking high anticholinergic burden drugs for just three years had a 54% higher risk of dementia.
Some common anticholinergics you might not realize are in your medicine cabinet include diphenhydramine (Benadryl), oxybutynin (Ditropan), and even some sleep aids. They’re not all prescription—many are sold over the counter. But that doesn’t mean they’re safe for long-term use. If you’re over 65, or if you’re taking more than one of these, talk to your doctor about alternatives. There are newer bladder medications that don’t cross the blood-brain barrier, and non-drug options like pelvic floor therapy can help too. Even small switches can cut your risk.
The posts below dive into real-world issues tied to these drugs: how side effects show up, how to spot dangerous combinations, and why some patients end up on too many at once. You’ll find guides on tracking medication lists, understanding drug safety alerts, and recognizing when a side effect is more than just a nuisance. Whether you’re managing your own meds or helping someone else, this collection gives you the tools to ask the right questions and avoid hidden risks.